 |
|
|
|
|||
 |
||||
AIM-7 Sparrow
 Mission:The
AIM-7 Sparrow is a radar-guided, air-to-air missile with a high-explosive
warhead. The versatile Sparrow has all-weather, all-altitude
operational capability and can attack high-performance aircraft
and missiles from any direction. It is a widely deployed missile
used by U.S. and NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) forces.
Mission:The
AIM-7 Sparrow is a radar-guided, air-to-air missile with a high-explosive
warhead. The versatile Sparrow has all-weather, all-altitude
operational capability and can attack high-performance aircraft
and missiles from any direction. It is a widely deployed missile
used by U.S. and NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) forces.
Features:The missile has five major sections: radome, radar guidance system, warhead, flight control (autopilot plus hydraulic controlsystem), and solid-propellant rocket motor. It has a cylindrical body with four wings at mid-body and four tail fins. Although external dimensions of the Sparrow remained relatively unchanged from model to model, the internal components of newer missiles represent major improvements with vastly increased capabilities.
Background:The AIM-7F joined the Air Force inventory in 1976 as the primary medium-range, air-to-air missile for the F-15 Eagle.
The AIM-7M, the only current operational version, entered service in 1982. It has improved reliability and performance over earlier models at low altitudes and in electronic countermeasures environments. It also has a significantly more lethal warhead. The latest software version of the AIM-7M is the H-Buildwhich has been produced since 1987 and incorporates additional improvements in guidance. The F-15 Eagle and F-16 Fighting Falcon fighters carry the AIM-7M Sparrow. U.S. and NATO navies operate a surface-to-air version of this missile called the RIM-7F/M Sea Sparrow.
In the Persian Gulf war, the radar-guided AIM-7 Sparrow proved to be a potent air-to-air weapon used by Air Force fighter pilots. Twenty-two Iraqi fixed-wing aircraft and three Iraqi helicopters were downed by radar-guided AIM-7 Sparrow missiles.
General Characteristics:
Primary Function: Air-to-air guided missile
Contractor: Raytheon Co.
Power Plant: Hercules MK-58 solid-propellant rocket motor
Thrust: Classified
Speed: Classified
Range: Classified
Length: 12 feet (3.64 meters)
Diameter: 8 inches (0.20 meters)
Wingspan: 3 feet, 4 inches (1 meter)
Warhead: Annular blast fragmentation warhead
Launch Weight: Approximately 500 pounds (225 kilograms)
Guidance System: Raytheon semiactive on either continuous wave
or pulsed Doppler radar energy
Date Deployed: 1976
Unit Cost: Approximately $125,000
Inventory: Classified
AIM-9 Sidewinder
 Services:
Navy, Marine Corps and Air Force
Services:
Navy, Marine Corps and Air Force
Description: The
AIM-9 Sidewinder is a heat-seeking, short-range, air-to-air missile
carried by fighter aircraft.
Features: The Sidewinder has a high-explosive warhead and an infrared heat-seeking guidance system. Its main components are an infrared homing guidance section, an active optical target detector, a high-explosive warhead and a rocket motor. The guidance section enables the missile to home in on the engine exhaust of target aircraft. An infrared unit costs less than other types of guidance systems and can be used day or night in all weather conditions. The infrared seeker also permits the pilot to launch the missile then leave the area or take evasive action while the missile guides itself to the target.
Background: A prototype of the Sidewinder, the AIM-9A, was first fired successfully in September 1953. The initial production version, designated AIM-9B, entered operational use in 1956 and has been improved upon steadily since. The L model was the first Sidewinder with the ability to attack from all angles, including head-on. The AIM-9M, currently the only one operational, has the all-aspect capability of the L model while providing all-around higher performance. The M model has improved defense against infrared countermeasures, enhanced background discrimination capability, and a reduced-smoke rocket motor. These modifications increase its ability to locate and lock on a target and decrease the missile's chances for detection. Deliveries began in 1983. The AIM-9M-7 was a specific modification to AIM-9M in response to threats expected in the Persian Gulf war zone. The AIM-9M and AIM-9X are future variants presently under development.
The Sidewinder is the most widely used air-to-air missile in the West, with more than 110,000 missiles produced for 27 nations excluding the United States. The AIM-9 is one of the oldest, least expensive and most successful missiles in the entire U.S. weapons inventory.
General Charateristics:
Primary Function: Air-to-air missile
Contractor: Raytheon Co.; Ford Aerospace and Communications Corp.;
Loral
Power Plant: Thiokol Hercules and Bermite MK 36 Mod 11; single-stage,
solid-propellant rocket motor
Length: 9 feet 6 inches (2.89 meters)
Diameter: 5 inches (.13 meters)
Fin Span: 2 feet 1 inch (0.63 meters)
Speed: Supersonic
Warhead: Blast fragmentation (conventional) weighing 20.8 pounds
(9.36 kg)
Launch Weight: 190 pounds (85.5 kg)
Range: 10+ miles (8.7 nautical , 16 km)
Guidance System: Solid-state infrared homing system
Unit Cost: $41,300
Date Deployed: 1956
|
Seeker: Active radar The AMRAAM /Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile/ was designed to replace the disappointing AIM-7 Sparrow. It is guided by an active pulse-doppler radar and propelled by a high-speed, reduced smoke rocket. The AMRAAM can acquire its targets beyond visual range /BVR/ and be launched at any aspect angle and speed. The AIM-120 is untested in actual combat. |
|
|
Seeker: TV with magnification Speed: Mach 0.65 Length: 8 ft 2 in Weight: 464 lb Warhead: 125 lb shaped charge Range: 0.6 to 14 miles Diameter: Drag factor: 46 |
|
|
Seeker: Passive radar Speed: Length: 13 ft 9 in Weight: 807 lb Warhead: 145 lb fragmentation Range: 30 miles Diameter: Drag factor: 46 |
|
The AGM-88A HARM /High Speed Anti-Radiation Missile/ is an upgrade of the Shrike. Towards the end of the Vietnam War, enemy radar operators learned to turn off the radar when they detected a Shrike missile launch. The HARM was developed with a much higher speed and range so it could hit a radar source without warning. It also has a better target acquisition system that is effective against both CW and pulse-dopppler radar. Both the enemy SA-8 Gecko and the allied Roland SAM systems use pulse-doppler radar.
AGM-84D Harpoon
 The AGM-84D Harpoon is an all-weather,
over-the-horizon, anti-ship missile system produced by McDonnell
The AGM-84D Harpoon is an all-weather,
over-the-horizon, anti-ship missile system produced by McDonnell
Douglas. Its low-level, sea-skimming cruise trajectory, active
radar guidance, and warhead design assure high survivability
and effectiveness.
Originally developed for the Navy to serve as its basic anti-ship missile for fleetwide use, the AGM-84D Harpoon also has been adapted for use on Air Combat Command's B-52G bombers. The 42nd Bombardment Wing, Loring Air Force Base, Maine, was first tasked to perform the Harpoon mission in 1985. The wing refined tactics and doctrine to merge the long-range, heavy-payload capability of the B-52 with the proven reliability of this superior stand-off attack weapon. These combine to provide the war-fighting capability to interdict ships at ranges well beyond those of other aircraft.
Features:
The AGM-84D Harpoon has been adapted for use on B-52G bombers, which can carry from eight to 12 missiles.
Specifications:
Primary Function: Air-to-surface
anti-ship missile
Contractor: McDonnell Douglas
Power Plant: Teledyne Turbojet
Thrust: 660 pounds
Length: 12 feet, 7 inches
Weight: 1,145 pounds
Diameter: 13.5 inches
Wing Span: 3 feet
Range: Over the horizon
Speed: High subsonic
Guidance System: Sea-skimming cruise using radar altimeter; active
radar terminal homing
Warheads: Penetrating high-explosive (488 lb)
Date Deployed: 1985
Air Force Inventory: Classified
AGM-84E SLAM
 The AGM-84D Harpoon is an all-weather,
over-the-horizon, anti-ship missile system. The AGM-84E Harpoon/SLAM
is an infrared Stand-Off Land Attack Missile used for long range
precision strikes.
The AGM-84D Harpoon is an all-weather,
over-the-horizon, anti-ship missile system. The AGM-84E Harpoon/SLAM
is an infrared Stand-Off Land Attack Missile used for long range
precision strikes.
Features:
The Harpoon's active radar guidance, warhead design, and low-level, sea-skimming cruise trajectory assure high survivability and effectiveness. The missile is capable of being launched from surface ships, submarines, or (without the booster) from aircraft. The AGM-84D has been adapted for use on Air Force B-52G bombers, which can carry from eight to 12 of the missiles. The AGM-84E uses an inertial navigation system with GPS, and is fitted with a Tomahawk warhead for better penetration.
Background:
Originally developed for the Navy to serve as its basic anti-ship missile for fleetwide use, the AGM-84D also has been adapted for use on the Air Force's B-52G bombers. The AGM-84D was first introduced in 1977, and in 1979 an air-launched version was deployed on the Navy's P-3 Orion aircraft. The AGM-84E has been developed for the Navy for land attack use.
General Characteristics:
Primary Function:Air, surface,
or submarine launched anti-surface (anti-ship) cruise missile.
AGM-85E; surface launched,precision land attack cruise missile.
Contractor:McDonnell Douglas
Power Plant:Teledyne Turbojet and solid propellant booster for
surface and submarine launch.
Thrust:660 pounds (approximately 594 kilograms)
Length: 12 feet, 7 inches (3.79 meters) -- air launched; 15 feet
(4.55 meters) -- surface and submarine
launched. SLAM; 14 feet, 8 inches (4.49 meters)
Weight: 1,145 pounds (515.25 kilograms) -- air launched; 1,470
pounds (661.5 kilograms) -- SLAM 1,385
pounds (629.55 kilograms) -- submarine or ship launched from
box or canister launcher.
Diameter: 13.5 inches (34.29 centimeters)
Wing Span: 3 feet (91.44 centimeters) with booster fins and wings.
Range:Over-the-horizon, in excess of 60 nautical miles.
Speed:High Subsonic
Guidance:Sea-skimming cruise monitored by radar altimeter, active
radar terminal homing. SLAM: Inertial
navigation with GPS, infrared terminal guidance.
Warhead:Penetration high-explosive blast (488 pounds/224 kilograms)
Unit Cost:$720,000
Date Deployed: 1985; SLAM 1993
|
AGM-62 Walleye Length: 3.05 m Diameter: 203 mm Wing Span: 0.91 m Weight:1089 kg Guidance: TV Warhead: - Range: 35 NM Date Deployed:1965 Speed: freefall |
 |
Type: 500 lb class general-purpose iron bomb
Length: 7 ft 2 in
Weight: 531 lb
Warhead: 275 lb H-6 high-explosive
Drag factor: 40
Simple, cheap and effective, the Mk series of general-purpose bomps usualy makes up the bulk tonnage of munitions dropped in any engagement. The Mk82 is effective against tanks and other ground force targets as well as small buildings.
|
Type: 500 lb class high-drag
iron bomb The Snakeye version of the Mk82 has drag fins which open upon release to rapidly decelerate the bomb. This causes the bombs to hit well behind the plane, allowing a safe egress from a low drop. This bomb is otherwise the same as the Mk82. |
|
|
Mk83 The Mk83 bomb is effective against madium to small buildings, storage tanks and warehouses. |
 |
Type: 2,000 lb class general-purpose iron bomb
Length: 12 ft 9 in
Weight: 1,972 lb
Warhead: 945 lb H-6 high-explosive
Drag factor: 60
The Mk84 is tha largest bomb in the Falcon arsenal. It is effective against large buildings, factories, power plants, bridges, hardened aircraft shelters and bunkers.
|
Type: TV guided bomb The GBU-15 uses a TV or imaging infrared seeker to lock onto its target, then glides to the point of impact using control fins. The GBU should be used for important and hard to destroy targets like command bunkers, hardened aircraft shelters and nuclear weapons plants. In addition, it can be used against targets in civilian areas, The warhead of the GBU-15 is the same as the Mk84. |
|
CBU-84 Cluster Bomb
Unit
Type: Sub-munitions
dispenser
Length: 7 ft 8 in
Weight: 960 lb
Warhead: 202 combined-effect bomblets
Drag factor: 50
The CBU-84 has fins to spin the unit at high velocity and disperse
the released bomblets over a wide area. Each bomblet contains
a half-pound forward-firing, shaped charge and a zirconium incendiary
ring. This munition is effective against light armor, infantry
and other soft targets.
BLU-107/B Durandal
Type: Anti-runway
cratering bomb
Length: 8 ft 2 in
Weight: 450 lb
Warhead: 330 lb high-explosive
Drag factor: 40
The Durandal was designed solely for the purpose of destroying
runways. The bomb first penetrates the runway surface and then
a delayed explosion buckles a large portion of the runway - damage
much more difficult to repair than the crater of a general-purpose
bomb. Note that a bomb hit toward the end of a runway might not
destroy enough pavement to put the runway completly out of action.
Texas Instruments PAVEWAY
Laser Guided Bomb GBU-22
DALLAS (September
25, 1996) - Texas Instruments (TI) Defense Systems & Electronics
(DS&E) has successfully qualified the PAVEWAY III Laser Guided
Bomb (LGB) Guided BombUnit (GBU) 22 on the F-16 aircraft. Testing,
which was funded by the company, was conducted by the United
States Air Force (USAF) from April 1996 to June 1996 at Eglin
Air Force Base, Florida. The test program included two guided
GBU-22 weapon releases, both successful. This member of the family
of PAVEWAY LGBs, the GBU-22, employs the Mk-82 500 pound warhead.
For the PAVEWAY family of LGBs, TI manufactures the laser seeker, guidance electronics, and control section, called the Guidance and Control Unit (GCU), which is attached to the front of the selected warhead. TI also produces the cruciform airfoil group, a tail section equipped with four pop-out wings to help stabilize the weapon during its flight. The adapter group, consisting of the ounting lugs for the bomb rack on top of the weapon, complete the TI-produced LGB kit.
The PAVEWAY family of LGBs is the world standard Laser Guided Bomb. During Operation Desert Storm, PAVEWAY LGBs were used to destroy enemy command and control facilities, bridges, SCUD ballistic missile launchers, and tanks. Over 10,000 LGBs were dropped during the ampaign by coalition forces. PAVEWAY was also successfully employed by NATO forces in Operation Deliberate Force in Bosnia because of its pin-point accuracy and reduced chances of collateral damage.
MK- 76
 The Mk 76 Mod 5 is a 25-pound, solid-metal
cast practice bomb. Its body is teardrop shaped and centrally
The Mk 76 Mod 5 is a 25-pound, solid-metal
cast practice bomb. Its body is teardrop shaped and centrally
bored to permit the insertion of a practice bomb signal cartridge.
The after body, which covers the tail tube, is
crimped to the bomb body and has welded-on conical tail fins.
The bomb is designed with single lug
suspension, using the Mk 14 suspension lug.
The Mk 76 Mod 5 practice bomb
is designed for impact firing only. It uses the Mk 1 firing pin
assembly to
initiate the signal cartridge. The signal cartridge and firing
pin assembly are held in place by means of a cotter pin.
Mk-106
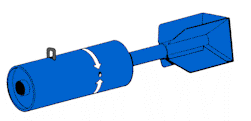 This 5-pound practice bomb is a thin-cased
cylindrical bomb used to simulate retarded weapon delivery. The
This 5-pound practice bomb is a thin-cased
cylindrical bomb used to simulate retarded weapon delivery. The
bomb is composed of the bomb body, a retractable suspension lug,
a firing device, and box-type conical fins.
The firing device consists of
a safety pin, a firing pin head, a cotter pin, a spring, and
a disc. The firing pin head
is the main body of the device and is threaded so it can be screwed
into the forward end of the bomb body.
The spring and the disc prevent the practice bomb signal cartridge
from striking the firing pin, located on the
face of the firing pin head, until it meets sufficient resistance
to force the cartridge into the firing pin. This
resistance is normally met when the weapon impacts the target,
but for added safety during ground handling,
the safety pin is installed into the firing pin head and secured
by a cotter pin. The safety pin and cotter pin are
removed before flight.
(Mk-82 SE, Mk-82 LD, Mk-83
LD, Mk-84 LD, Rockeye II, LAU-10, LAU-61, LAU-68, CBU-59)
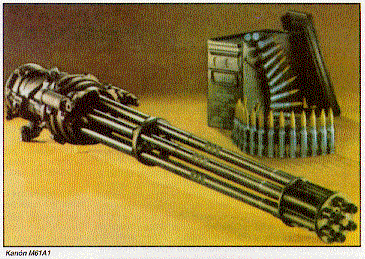
M61A1 Vulcan
|
GUN: externally powered six barrel,
20 mm Gatling Mounted in the nose of each F/A-18, is General Electric's 20 mm M61A1 Vulcan cannon. The gun operates on the same principle as other Gatling weapons and is hydraulically driven. It's primary purpose is for close-in visual identification air-to-air combat, and for air-to-ground close air support. The M61A1 Vulcan armament system has proven to be highly reliable. Design features that provide positive round control through the ammunition transfer cycle include: Highly refined design geometry
of sprockets, guides and round paths, |
  |




