|
|
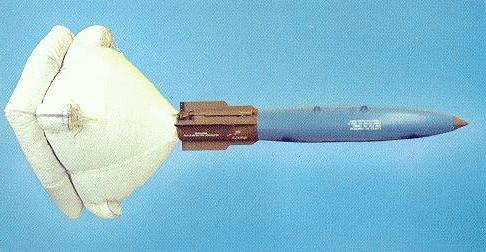
Mk20 Rockeye
|
Type: 500 lb class general-purpose
iron bomb Simple, cheap and effective, the Mk series of general-purpose bomps usualy makes up the bulk tonnage of munitions dropped in any engagement. The Mk82 is effective against tanks and other ground force targets as well as small buildings. |
 |
Mk82HD Snakeye
|
Type: 500 lb class high-drag
iron bomb
The Snakeye version of the Mk82 has drag fins which open upon release to rapidly decelerate the bomb. This causes the bombs to hit well behind the plane, allowing a safe egress from a low drop. This bomb is otherwise the same as the Mk82. |
|
Mk83
Mk84
|
Type: 2,000 lb class general-purpose
iron bomb The Mk84 is tha largest bomb in the Falcon arsenal. It is effective against large buildings, factories, power plants, bridges, hardened aircraft shelters and bunkers. |
 |
|
GBU-10 Paveway II 2000 lb GBU-12 Paveway II 500 lb GBU-16 Paveway II 1000 lb GBU-24 Paveway III 2000 lb GBU-24E/B Paveway III 2000 lb GPS guided |
|
GBU-15 Guided Bomb Unit
|
Type: TV guided bomb
The GBU-15 uses a TV or imaging infrared seeker to lock onto its target, then glides to the point of impact using control fins. The GBU should be used for important and hard to destroy targets like command bunkers, hardened aircraft shelters and nuclear weapons plants. In addition, it can be used against targets in civilian areas, The warhead of the GBU-15 is the same as the Mk84. |
|
|
JDAM is not intended to replace any existing weapon system; rather, it is to provide accurate delivery of general purpose bombs in adverse weather conditions. The JDAM will upgrade the existing inventory of Mk-83 1,000- and Mk-84 2,000-pound general purpose unitary bombs and the 2,000-pound hard target penetrator bomb by integrating a guidance kit consisting of an inertial navigation system/global positioning system guidance kit. The 1,000-pound variant of JDAM is designated the GBU-31, and the 2,000-pound version of the JDAM is designated the GBU-32. JDAM variants for the Mk-80 250-pound and Mk-81 500-pound bombs are designated GBU-29 and GBU-30, respectively. Hard Target penetrators being changed into low-cost JDAMs included the 2,000 pound BLU-109 and 1,000 pound BLU-110. The JDAM will be continuously
updated by aircraft avionics systems prior to release. Once released,
the bomb's INS/GPS will take over and guide the bomb to its target
regardless of weather. Guidance is accomplished via the tight
coupling of an accurate GPS with a 3-axis INS. The Guidance Control
Unit provides accurate guidance in both GPS-aided INS modes of
operation and INS-only modes of operation. This inherent JDAM
capability will counter the threat from near-term technological
advances in GPS jamming. The weapon system allows launch from
very low to very high altitude and can be launched in a dive,
toss, loft or in straight and level flight with an on-axis or
off-axis delivery. JDAM also allows multiple target engagements
on a single pass delivery. JDAM provides the user with a variety
of targeting schemes, such as preplanned and inflight captive
carriage retargeting. |
|
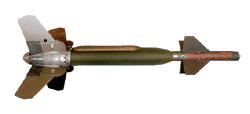
CBU-84 Cluster Bomb Unit
|
Type: Sub-munitions dispenser Length: 7 ft 8 in Weight: 960 lb Warhead: 202 combined-effect bomblets Drag factor: 50 |
The CBU-84 has fins to spin the unit at high velocity and disperse the released bomblets over a wide area. Each bomblet contains a half-pound forward-firing, shaped charge and a zirconium incendiary ring. This munition is effective against light armor, infantry and other soft targets. |
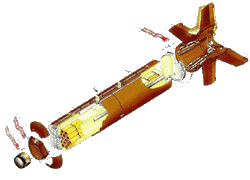
CBU-87/B Combined Effects Munitions (CEM)
BLU-97/B Combined Effects Bomb (CEB)
|
Contractor Aerojet General / Honeywell
Weight: 950 pounds Length: 92 inches Diameter: 15.6 inches Guidance: None Control: Spin [6 selections] Autopilot: None Propulsion: None Warhead: 202 BLU-97/B Combined Effects Bomb (CEB) anti-personnel / anti-materiel shaped-charge fragmentation & incendiary Fuse: Integral part of dispenser 12 time selections FZU-39/B proximity sensor 10 height-of-burst selections |
 |
||
|
The CBU-87 is a 1,000-pound, Combined Effects Munition (CEM) for attacking soft target areas with detonating bomblets. The CBU-87 CEM, an all-purpose, air-delivered cluster weapons system, consists of a SW-65 Tactical Munitions Dispenser (TMD) with an optional FZU-39 proximity sensor. The BLU-97/B Combined Effects Bomb (CEB), effective against armor, personnel and material, contains a shaped charge, scored steel casing and zirconium ring for anti-armor, fragmentation and incendiary capability. The bomblet case is made of scored steel designed to break into approximately 300 preformed ingrain fragments for defeating light armor and personnel. A total of 202 of these bomblets are loaded in each dispenser enabling a single payload attack against a variety and wide area coverage. The footprint for the CBU-87 is approximatel 200 meters by 400 meters. The body of the submunition is cylindrical in shape, approximately 20 centimeters long, and has a 6 centimeter diameter. It is bright yellow when new. During Desert Storm the US Air Force dropped 10,035 CBU-87s. During Allied Force the US dropped about 1,100 cluster bombs, and most of these were CBU-87s. The dud rate for a standard cluster was approximately five percent. |
|||
|
Contractor Aerojet General / Honeywell
Weight: 710 pounds Length: 92 inches Diameter: 16 inches Guidance: None Control: none Autopilot: None Propulsion: None Warhead: 72 BLU-91/B anti-tank 22 BLU-92/B anti-personnel Fuse: Integral part of dispenser FZU-39/B proximity sensor |
The CBU-89 Gator Mine, a 1,000-pound
cluster munition containing antitank and antipersonnel mines,
consists of a SUU-64 Tactical Munitions Dispenser with 72 antitank
mines, 22 antipersonnel mines, and an optional FZU-39 proximity
sensor. Mine arming begins when the dispenser opens. Mine detonation
is initiated by target detection, mine disturbance, low battery
voltage, and a self-destruct time-out. The antitank mine is a
magnetic sensing submunition effective against tanks and armored
vehicles. The antipersonnel mine has a fragmenting case warhead
triggered by trip wires. The US Air Force employed 1,105 CBU-89s
during the Gulf War. The Gator mine system provides a means to emplace minefields on the ground rapidly using high-speed tactical aircraft. The minefields are used for area denial, diversion of moving ground forces, or to immobilize targets to supplement other direct attack weapons. |
|
Gator consists of two companion systems. The Air Force CBU-89/B is a 1000-pound class cluster weapon using the SUU-64/B Tactical Munitions Dispenser (TMD). The TMD is the same general configuration used for the CBU-87/B Combined Effects Munition. This commonality allows for high-rate, low-cost production of the dispenser. The Navy CBU-78/B is a 500-pound class cluster weapon that uses the Mk7 Rockeye dispenser. Rockeye has been in high-rate production for many years; the Mk7 dispenser is also a low-cost item. Both systems contain a mix of
BLU-91 /B antitank (AT) and BLU-92/B antipersonnel (AP) mines
-- 72 AT and 22 AP for the CBU-89/B; 45 AT and 15 AP for the
CBU-78/B. Commonality of mines for both systems also contributes
to high-rate, low-cost production. The BLU-91 /B AT mine is the
heart of the Gator system. Microelectronics in each mine detect
targets, discriminate armored vehicles, and detonate the mine
when the target reaches the most vulnerable approach point. A
Misznay-Schardin explosive charge defeats the belly armor of
most vehicles. The BLU-92/B AP mine serves to discourage minefield
clearing. Upon activation, the AP mine explosion sends high-velocity
fragments in a horizontal plane over a wide area. The size of the Gator minefield is determined by the opening height of the dispenser. After dispenser opening, the mines are self-dispersed using aerodynamic forces. The mine pattern on the ground is directly proportional to opening altitude, which is controlled by either the dispenser electromechanical faze or an optional proximity sensor. Aerojet Ordnance Company (AOC) is the system integration prime contractor for Gator. All elements of the system are either procured by Aerojet or furnished by the US Government. The company is responsible for total system performance, including live testing. Each month three Gator systems are randomly selected from the production line and flight tested. Aerojet Ordnance Company warrants system performance for five years, assuring Gator reliability. |
|
BLU-107/B Durandal
|
Type: Anti-runway cratering bomb Length: 8 ft 2 in Weight: 450 lb Warhead: 330 lb high-explosive Drag factor: 40 |
 |
|
The Durandal was designed solely for the purpose of destroying runways. The bomb first penetrates the runway surface and then a delayed explosion buckles a large portion of the runway - damage much more difficult to repair than the crater of a general-purpose bomb. Note that a bomb hit toward the end of a runway might not destroy enough pavement to put the runway completly out of action. |
|
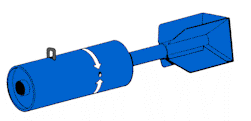 This 5-pound practice bomb is a thin-cased
cylindrical bomb used to simulate retarded weapon delivery. The
bomb is composed of the bomb body, a retractable suspension lug,
a firing device, and box-type conical fins.The firing device
consists of a safety pin, a firing pin head, a cotter pin, a
spring, and a disc. The firing pin head is the main body of the
device and is threaded so it can be screwed into the forward
end of the bomb body. The spring and the disc prevent the practice
bomb signal cartridge from striking the firing pin, located on
the face of the firing pin head, until it meets sufficient resistance
to force the cartridge into the firing pin. This This 5-pound practice bomb is a thin-cased
cylindrical bomb used to simulate retarded weapon delivery. The
bomb is composed of the bomb body, a retractable suspension lug,
a firing device, and box-type conical fins.The firing device
consists of a safety pin, a firing pin head, a cotter pin, a
spring, and a disc. The firing pin head is the main body of the
device and is threaded so it can be screwed into the forward
end of the bomb body. The spring and the disc prevent the practice
bomb signal cartridge from striking the firing pin, located on
the face of the firing pin head, until it meets sufficient resistance
to force the cartridge into the firing pin. Thisresistance is normally met when the weapon impacts the target, but for added safety during ground handling, the safety pin is installed into the firing pin head and secured by a cotter pin. The safety pin and cotter pin are removed before flight. |
|
|
Class 2,000 lb. Penetrator, Blast/Fragmentation
Guidance Ballistic Control Low Drag Fins/Air Foil Groups Autopilot: None Propulsion: None Weight (lbs.) 1950 Length (in.) 98.54 Diameter (in.) 14.5 Explosive 535 lbs. Tritonal Fuze FMU-143 Series Stabilizer Fins and Airfoil Groups (Laser Guided Bombs) Contractor Lockheed Missiles & Space Unit Cost $2,126 (Warhead Only) Aircraft F-117 F-15E F-16A-D F-111D-F |
|
| The BLU series bomb bodies use PBNX-109 as explosive filler. The BLU-109A/B used with the GBU-24 and GBU-31(V)4/B is a special purpose bomb comprised of steel alloy used for hardened targets. The BLU-109/B (I-2000) is an improved 2,000-pound-class bomb designed as a penetrator without a forward fuze well. Its configuration is relatively slim, and its skin is much harder than that of the standard MK-84 bomb. The skin is a single-piece, forged warhead casing of one-inch, high-grade steel. Its usual tail fuze is a mechanical-electrical FMU- 143. The 1,925-pound bomb has a 550-pound tritonal high-explosive blast warhead. The BLU-109/B was always mated with a laser guidance kit to form a laser-guided bomb in Desert Storm. | |
| Practice ordnance includes 25-pound BDU-33 bombs having a spotting charge that releases a cloud of smoke on impact. The BDU-33 is used to simulate the MK 82 in low drag configuration. The munitions to be loaded onto aircraft are brought to the flightline on a trailer. The BDU-33 bombs are lifted out of a metal cage on a trailer and are locked in place underneath the aircraft. The BDU-33 bombs are lifted out of a cage on the trailer and carried to the aircraft 20 feet away. BDU-33 munitions are loaded onto TERs (Triple Ejector Racks) and SUUs (Suspension Units). The BDU-33 is pushed against a spring loaded catch and locked into place. The unloading of the BDU-33 from the aircraft involves loosening the bolts and releasing the spring. The BDU-33 is carried back to the trailer. | |
|
Destructor Mines are general purpose
low-drag bombs converted to mines. They can be deployed by air,
either at sea as bottom mines or on land as land mines. With
the MK 75 Modification Kit installed, a MK 82 bomb (500 pounds)
becomes a MK 36 DST. The conflict in Southeast Asia saw the introduction of a different kind of mine called a Destructor (DST). Destructors Mk 36, Mk 40, and Mk 41 are aircraft-laid bottom mines which use General Purpose (GP) Low-Drag Bombs Mk 82, Mk 83, and Mk 84, respectively as the mine case and explosive charge. The bombs are converted to mines with the installation of a kit of modular components that comprise a mine-type arming, detector, and firing system. The kit contains an arming device, an explosive booster, a magnetic-influence firing mechanism and associated hardware. The arming device and booster install in the bomb's nose cavity and the firing-mechanism (with battery) installs in the bomb¹s tail cavity. The same kit of components and method of assembly are used for each one of the destructors, but the kits are available in a number of configurations, each with a different circuitry to meet a variety of operational requirements. It should be noted, however, that since the bomb cases are small, medium, and large, they require different flight gear. DST¹s became the first mines to be used on both land and sea. When dropped on land, they bury themselves in the ground on impact, ready to be actuated by military equipment, motor vehicles and personnel. When dropped in rivers, canals, channels, and harbors, they lie on the bottom ready to be actuated by a variety of vessels including war ships, freighters, coastal ships, and small craft. |
|
| The CBU-52, -58 and -71 all use SUU-30 dispensers, a metal cylinder divided longitudinally. One-half contains a strong back section that provides for forced ejection and sway-bracing. The two halves lock together. Four cast aluminum fins are attached at a 9~degree angle to the aft end of the dispenser and are canted 1.25 degrees to impart spin-stabilized flight. When released from the aircraft, the arming wire/lanyard initiates the fuze arming and delay cycle. At fuze function, the fuze booster ignites and unlocks the forward end of the dispenser. Ram air action on the dispenser forces the two halves apart, instantaneously dispensing the payload and allowing the bomblets to spin-arm and self-dispense. A total of 17,831 were expended during the Gulf War. | |
[ A-A missiles ] [ A-G missiles ] [ Free-fall munition ] [ Other ] [ Armament ] [ Home ]